Age Gracefully
Ageing is a continuous, irreversible, universal process, which starts from conception till the death of an individual. However, the age at which one’s productive contribution declines and one tends to be economically dependent can probably be treated as the onset of the aged stage of life. National Elderly Policy defines person of 60+ age group as elderly.
India is facing several challenges in the form of weak economic growth, weak pension system, and null infrastructure for ageing people, and above all lack of political will makes life miserable for the senior citizens in India. Problems of aging usually appear after the age of 60 years.
People worldwide are living longer compared to earlier. Today, for the first time in history, most people can expect to live into their sixties and beyond and by 2050, the world’s population aged 60 years and older is expected to total 2 billion, up from 900 million in 2015. Today, 125 million people are aged 80 years or older. By 2050, there will be almost this many (120 million) living in China alone, and 434 million people in this age group worldwide. By 2050, 80% of all older people will live in low and middle-income countries. Life expectancy is going-up year on year.
Life expectancy at birth
Among the challenges which India faces, UNPF report says the feminization of ageing remained a key one. The sex ratio of the elderly has increased from 938 women to 1,000 men in 1971 to 1,033 in 2011 and is projected to increase to 1,060 by 2026. The report also noted that between 2000 and 2050, the population of age 80-plus people would have grown 700% “with a predominance of widowed and highly dependent very old women” and so the special needs of such old women would need significant focus of policy and programmes.
 Source: Bloom & Luca, 2016
Source: Bloom & Luca, 2016
Proportion of elderly population
Among the challenges which India faces, UNPF report says the feminization of ageing remained a key one. The sex ratio of the elderly has increased from 938 women to 1,000 men in 1971 to 1,033 in 2011 and is projected to increase to 1,060 by 2026. The report also noted that between 2000 and 2050, the population of age 80-plus people would have grown 700% “with a predominance of widowed and highly dependent very old women” and so the special needs of such old women would need significant focus of policy and programmes.
 Source: Bloom & Luca, 2016
Source: Bloom & Luca, 2016
Population figures on ageing
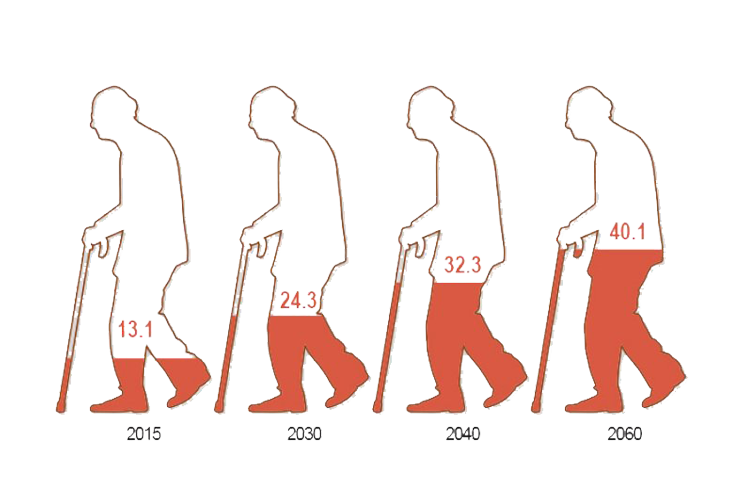
Age division of Indian population (0-14) is 30.8%, (15-59) is 60.3%, (60+) is 8.6%. According to Population Census 2011, there are nearly 104 million elderly persons in India. It has increased from 5.5% in 1951 to 8.6% in 2011. Projected a rise upto 19% in 2050. As regards rural and urban areas, more than 73 million persons i.e. 71% of elderly population resides in rural areas while 31 million or 29% of elderly population are in urban area.
Feminization of ageing
Among the challenges which India faces, UNPF report says the feminization of ageing remained a key one. The sex ratio of the elderly has increased from 938 women to 1,000 men in 1971 to 1,033 in 2011 and is projected to increase to 1,060 by 2026. The report also noted that between 2000 and 2050, the population of age 80-plus people would have grown 700% “with a predominance of widowed and highly dependent very old women” and so the special needs of such old women would need significant focus of policy and programmes.

Problems associated with old age
Social
Financial
Health
Social
Financial
Health
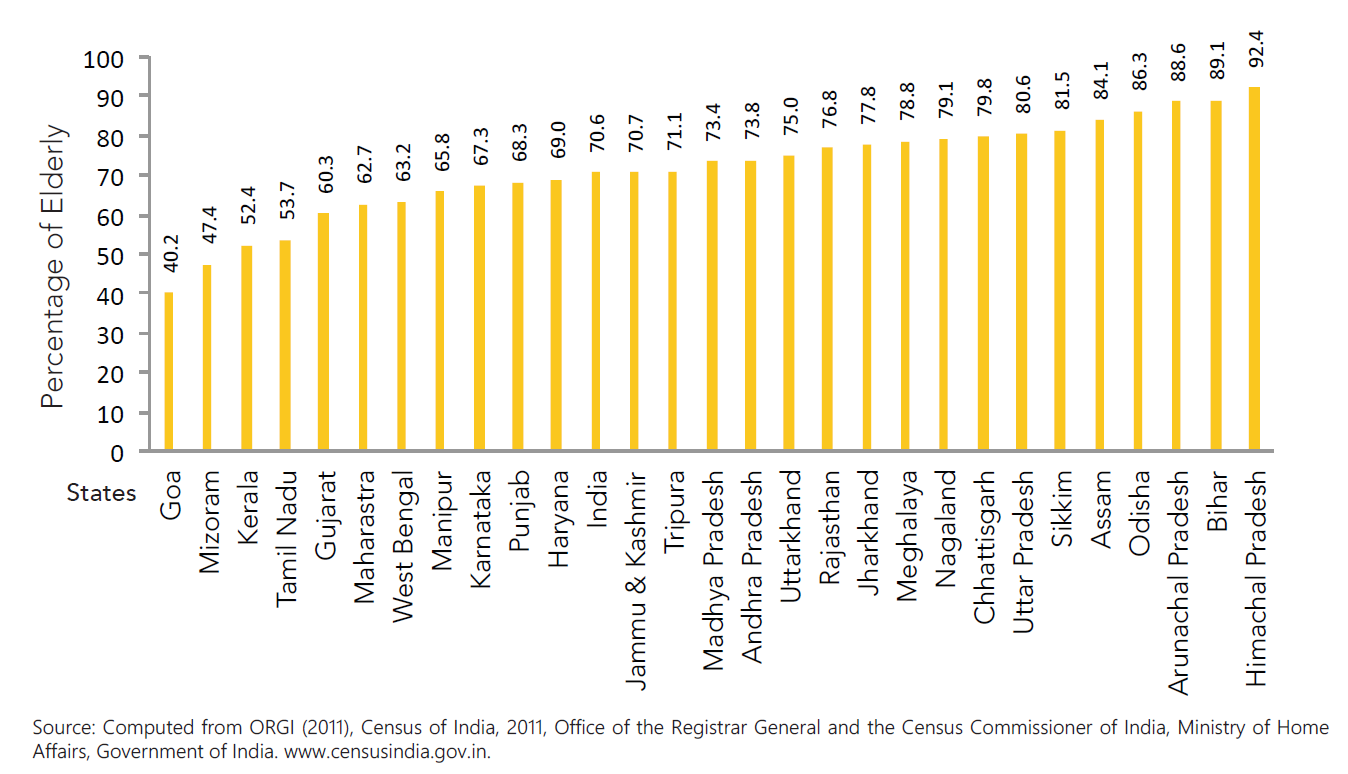
Proportion of older adults living in rural areas
How can one age gracefully?
There are multiple ways of gracefully ageing.
However, majority of senior citizens in India cannot afford this.
It is our endeavor to help the elderly. Elderly must be given a new task periodically, encourage social movements, Yoga and Meditation and prevent age associated complications like depression, neurological complications etc.,
It is our endeavor to help the elderly. Elderly must be given a new task periodically, encourage social movements, Yoga and Meditation and prevent age associated complications like depression, neurological complications etc.,
SNEHA has been working in the field of elderly since its inception. Numerous medical camps have been organized for the elderly and many cataract operations have been conducted.
Age Gracefully is an initiative taken up by SNEHA.
Donate liberally for the cause of senior citizens.